1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
|
## Enclosure Drawing
### Original Enclosure
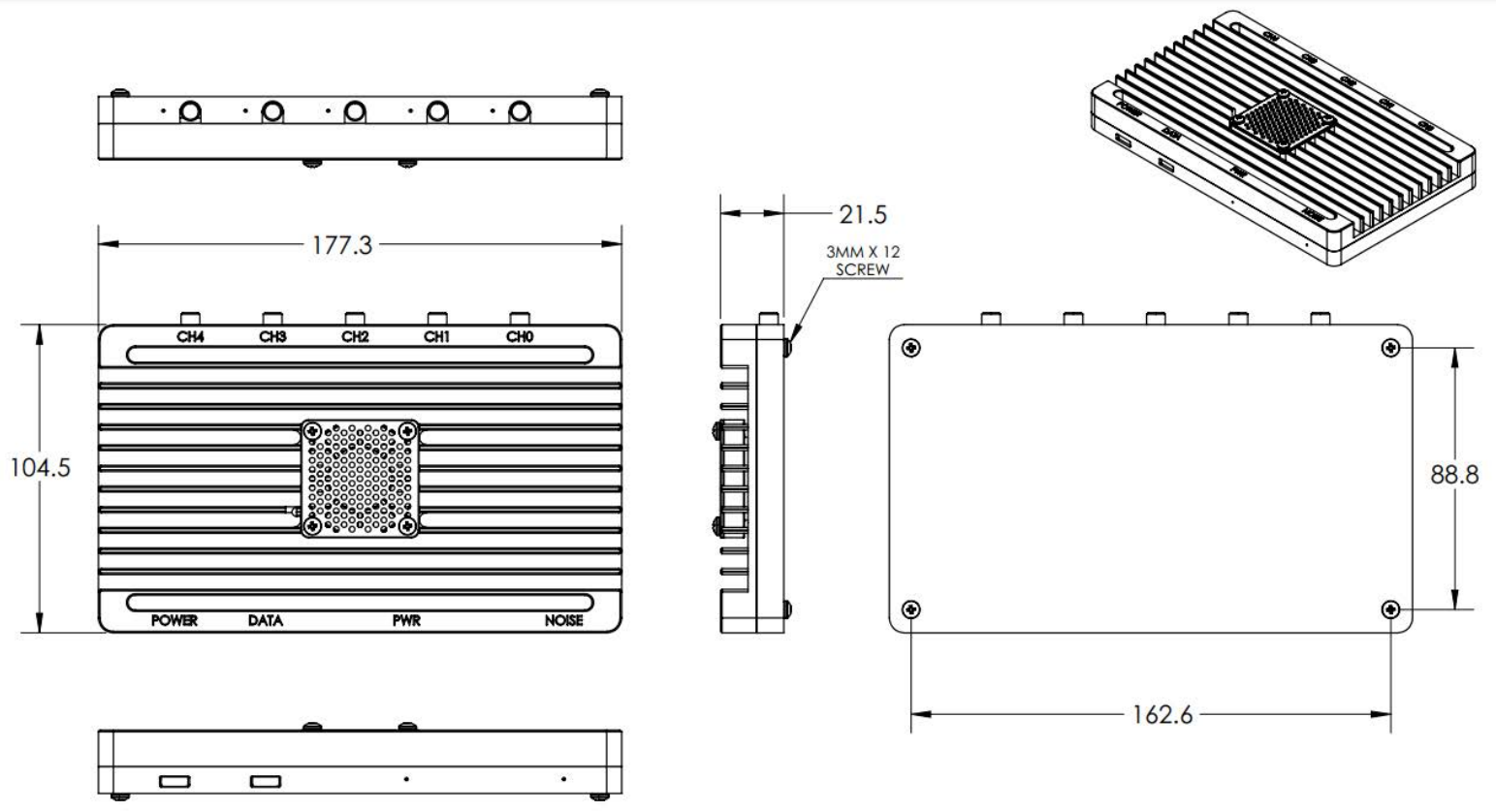
### New Enclosure

## SSH / Screen Login Details
The default login details for the KrakenSDR images we provide are as follows:
Username: krakenrf
Password: krakensdr
## Connecting to an Established WiFi Network
If you are using either the Kraken DF pre-made image on a fixed WiFi network, instead of using hotspots, then you will need to add your WiFi network details. To do so you will need to temporarily connect your Pi 4 to a monitor and keyboard or connect your Pi 4 using Ethernet and SSH into it.
The default login credentials for the terminal and SSH are krakenrf/krakensdr, port 22.
To add your network, edit the file: wpa_supplicant.conf
`sudo nano /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf`
Add your own network by adding the following text
```
network={
ssid="MY_WIFI_SSID"
psk="MY_WIFI_PASSWORD"
}
```
Then Press “CTRL+X”, “Y” to close and save the file. Now when you reboot the Pi 4 should automatically connect to your network.
On the Pi 5 simply use the network manager GUI in the desktop OS to change WiFi credential information.
## Editing the Mobile Hotspot Connection Credentials
On the Pi 4 image, to change the details of the mobile hotspot that the KrakenSDR will automatically connect to, edit wpa_supplicant.conf
`sudo nano /etc/wpa_supplicant/wpa_supplicant.conf`
change the SSID and psk password of the "KrakenAndroid" entry to your preferred credentials.
On the Orange Pi 5 and Raspberry Pi 5, simply use the built-in network manager GUI as part of the OS.
## Editing the Default Raspberry Pi 4 Hotspot Credentials
```
cd Autohotspot
sudo ./autohotspot-setup.sh
```
Select option 7 and follow the instructions.
## Port Forwarding
If you wish to make your KrakenSDR remotely accessible over the internet you will need to set your router to forward ports 8080 for the web interface, and port 8081 for the data output for external apps.
Instead of port forwarding, you may wish to investigate more modern VPN solutions like [Zerotier](https://www.zerotier.com/).
## Port Security
Be aware that if you expose port 8080 to the internet, then your KrakenSDR will be open to being controlled publicly by anyone with your IP address. Therefore, we do not recommend power forwarding port 8080 unless you have a specific purpose for doing so. In future software enhancements we will be adding a security option for this page.
If you plan on also exposing post 22 so that you can SSH into the device remotely, then we strongly recommend changing the SSH password from “krakensdr” to a custom password.
Again, instead of port forwarding, you could use something modern like Zerotier and avoid these security issues.
## Disabling the WiFi Hotspot
If you only want to use Ethernet, and you need to disable the WiFi hotspot from our ready to use image you can do so easily via an SSH connection. SSH into the KrakenSDR using the default krakenrf/krakensdr username/password. Then run the Autohotspot script.
```
cd Autohotspot
sudo ./autohotspot-setup.sh
```
Select option 4 "Uninstall Autohotspot of permanent access point". Then after that completes, select option 8 to exit. Now reboot, and the hotspot will be disabled.
## Data Output For Third Party Software
When set to the 'Kraken App' DOA Data Format the latest bearing data will be output to an HTML page at "http://PI4_IP_ADDR:8081/DOA_value.html" in the CSV format every update period.
The output format CSV ordering is as follows:
```
1. UNIX Epoch Time : (13 Digit LONG),
2. Max DOA Angle in Degrees in Compass Convention : (3 Digit 000 - 359, 90deg East),
3. Confidence Value : (0-99 float, higher indicates a better quality reading),
4. RSSI Power in dB : (0 dB is max power),
5. Channel Frequency in Hz,
6. Antenna Array Arrangement : ("UCA"/"ULA"/"Custom"),
7. Latency in ms : (Time from signal arrival at antenna, to result. NOT including network latency.),
8. Station ID : (Name of the KrakenSDR station inputted in the Station Information box in the Web GUI),
9. Latitude,
10. Longitude,
11. GPS Heading,
12. Compass Heading (if available),
13. Main Heading Sensor Used ("GPS"/"Compass"),
14-17. Reserved for possible future use,
18-377. Full 360 degrees DOA output. First element specifies DOA power output at 0 degrees, second element power at 1 degrees etc. NOTE: Uses unit circle convention, so due EAST is classed as 0 degrees, NORTH 90 degrees and so on. Needs to be rotated into compass convention.
```
If multiple VFO channels are used, each channel will output it's own unique CSV data from 1-377 separated by a newline character "\n".
## Changing Settings Programmatically
In the `~/krakensdr_doa/krakensdr_doa/_share` folder there is a file called `settings.json` where the current settings in the Web GUI are stored, including settings like the center frequency and gain.
An external piece of software can edit this file, and the software will automatically update it's settings to those specified once the file is changed.
It is up to you the programmer to ensure that the inputs are valid. Entering incorrect values may crash the software.
If you expect the Web GUI to be open and want the KrakenSDR Web GUI to automatically update when you make a change to the file, you will need to set the "ext_upd_flag" value to "true". It will automatically be written as false once the KrakenSDR web UI has been updated.
# Tested Devices
## Working
* Raspberry Pi 4
* Raspberry Pi 5
* Intel i5, i7 on Ubuntu
* Dell Wyse Thin Clients
* Orange Pi 4 - Note: The OPI4 is sensitive to USB cables. Needs a short high quality USB data cable. Will not work with long and/or poor quality USB data cables.
* Orange Pi 5 / 5B- Note that there is no WiFi on the standard device, but there is a '5B' version that includes WiFi which is recommended. For the Orange Pi 5 without WiFi we recommend using an M2 or PCIE add on card, rather than USB WiFi dongle. KrakenSDR may not work properly if the USB bandwidth is shared by another high bandwidth device like a WiFi stick.
* Beelink Mini S12 Mini PC 12th Gen N95
### Virtualization
* Virtual Box Ubuntu VM in Windows and Linux Hosts. (Be sure to use VirtualBox 7.0.0 for the best stability and USB3.0 must be enabled)
* Docker with ClearLinux
## Working but with major quirks
* Odroid N2/+ - Note: You must use the **BOTTOM USB port that is closest to the DC power barrel jack**. All other USB ports do not work for high data rate devices on this machine. Also requires a high quality USB cable. On this device every ~12 hours there is some USB glitch resulting in sample mis-alignment. This results in the DOA results going bad. If you have periodic recalibration turned ON (the default), it's not a huge deal, but you could be running for about 5 minutes with bad results.
## Not Working
* Tinkerboard - Unfortunately pure 32-bit ARM CPUs are not supported by Miniforge Conda.
# Making Kraken Autoboot
If you manually install the software you can use the same procedure that we use on our image files to make the software autoboot. Make sure to change any home directory paths appropriately for your own system.
Create a start_kraken.sh script in /boot:
```
#!/bin/bash
# This script is run on startup by a systemd service at /lib/systemd/system/krakensdr.service
cd /home/krakenrf/krakensdr_doa
./kraken_doa_start.sh
```
Create a systemd service called krakensdr.service in `/lib/systemd/system/krakensdr.service`:
```
[Unit]
Description=Start KrakenSDR Code
After=multi-user.target
[Service]
Type=forking
Workingdirectory=/home/krakenrf/krakensdr_doa
ExecStart=/usr/bin/sh /boot/start_kraken.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
```
Make the service boot on every restart:
```
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable krakensdr.service
```
Finally, in kraken_doa_start.sh, comment out the eval line, and uncomment the source line:
```
source /home/krakenrf/miniforge3/etc/profile.d/conda.sh #<- required for systemd auto startup
#eval "$(conda shell.bash hook)"
conda activate kraken
```
# KrakenSDR Manual Bias Tee Control
When using the KrakenSDR as a standard SDR, you can activate each individual bias tee using the rtl_biast and -g flag to select the correct GPIO. GPIO 0 is for the noise source. GPIO's 1,2,3,4,5 are for the bias tees.
For example to turn on the bias tee on the first port `rtl_biast -g1 -b1`.
|
